上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Screen Quest 荧光法多药物抗性MDR检测试剂盒 *1板*
| 货号 | 36340 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 100 Tests | 价格 | 2604 |
| Ex (nm) | 492 | Em (nm) | 514 |
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | ||
| 产品详细介绍 | |||
简要概述
肿瘤细胞对细胞药物的耐药性被认为是化疗成功的主要障碍之一。有些肿瘤最初是耐药的,对细胞抑制药物治疗没有反应;另一些肿瘤最初反应良好,但最终会再生并产生耐药性。这种现象可能是由所给抗肿瘤药物诱导的基因突变引起的,也可能代表恶性肿瘤中已存在的耐药细胞群的选择。多药耐药(MDR)是多种化疗失败的主要因素。在过去的几年中,人们普遍认为化疗耐药性与至少两个ATP依赖的药物外排的过度表达有关。这些细胞膜蛋白,称为P-糖蛋白(Pgp,MDR1)和多药耐药相关蛋白(MRP1)是ABC转运体家族的成员。我们的检测试剂盒使用荧光MDR指示剂来检测这两种MDR活性。这种疏水性荧光染料分子迅速穿透细胞膜并保留在细胞内。短时间培养后,细胞内游离染料浓度明显增加。在表达MDR1和/或MRP1的细胞中,该染料被MDR转运体挤压,从而降低细胞荧光强度。然而,当其挤压被干扰MDR1和MRP1活性的试剂阻断时,其细胞荧光强度明显增加。我们的MDR检测试剂盒提供了一个优化的检测方法的所有必须成分。该方法可在96孔或384孔微孔板中进行,且易于自动化。该试剂盒是高通量筛选MDR抑制剂或鉴定具有高水平MDR活性细胞的理想试剂盒。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的Screen Quest 荧光法多药物抗性MDR检测试剂盒。
适用仪器
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 490nm |
| 发射: | 525nm |
| cutoff: | 515nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 读取模式: | 底读模式 |
产品说明书
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 准备细胞
- 添加MDR抑制剂或化合物
- 添加MDR染料加载溶液(对于96孔板为100 µL /孔,对于384孔板为25 µL /孔)
- 在室温下孵育1小时
- 使用底部读取模式检测Ex / Em = 490/525 nm的荧光强度
溶液配制
储备溶液配制
MDR指示剂储备溶液:将20 µL(#36340-1板)或200 µL(#36341-10板)添加到MDR指示剂(组分A)中,并充分混合。 注意:20 µL MDR指示剂原液足以装满一块板。 未密封的MDR指示剂原液可以分装,并在<-20℃下保存1个月。 避光,并避免反复冻融。
工作溶液配制
MDR染料加载溶液:将20 µL的MDR指示剂储备溶液添加到10 mL的测定缓冲液(组分C)中,并充分混合。 注意:MDR染料加载溶液足以装满一块板,并且在室温下至少可稳定2小时。
实验步骤
- 通过将10 µL的10X(96孔板)或5 µL的5X(384孔板)化合物加入化合物缓冲液(如PBS或HHBS)中来处理细胞。对于空白孔(没有细胞的培养基),添加相应量的化合物缓冲液。注意:添加化合物之前不必洗涤细胞。但是,如果测试的化合物对血清敏感,则可以在添加化合物之前将生长培养基和血清因子吸掉。抽吸后,向孔中添加相同体积的HHBS(例如,对于96孔板为90 µL,对于384孔板为20 µL)。或者,细胞可以在无血清培养基中生长。
- 在室温下或在37℃,5%CO2的培养箱中孵育细胞板至少15分钟。
- 加入100 µL /孔(96孔板)或25 µL /孔(384孔板)的MDR染料加载溶液。
- 在避光条件下,于室温下孵育染料加载板1小时。注意:适当的孵育时间取决于所用的单个细胞类型和细胞浓度。注意:上样后请勿洗涤细胞。注意:对于非贴壁细胞,建议在孵育后以800 rpm离心细胞板2分钟。
- 使用底部读取模式检测Ex / Em = 490/525 nm的荧光强度。
图示
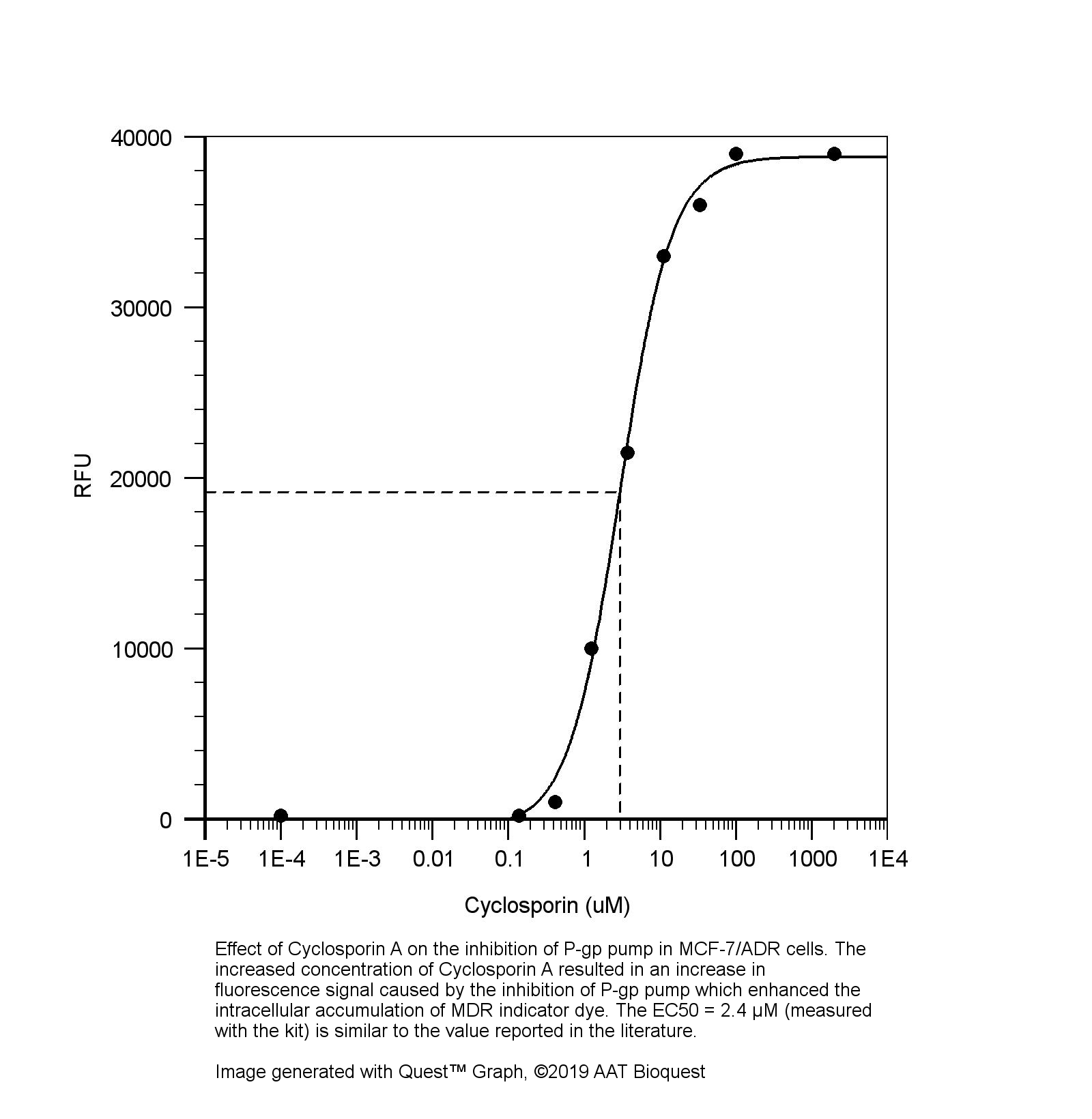
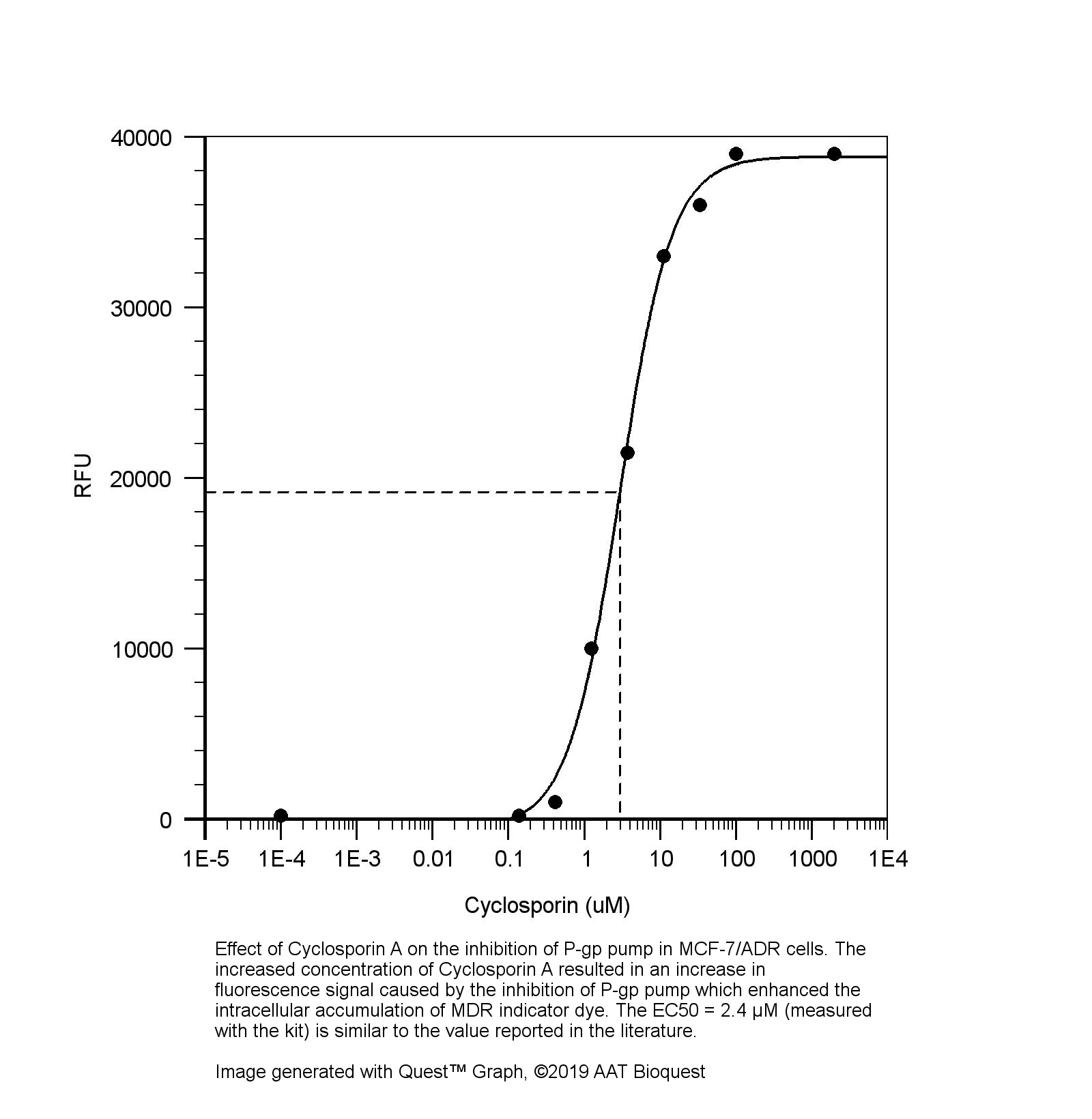 图1.环孢菌素A对MCF-7 / ADR细胞中P-gp的抑制作用。 环孢菌素A浓度的增加导致荧光信号的增加,这是由于P-gp的抑制所致,从而增强了MDR指示剂染料在细胞内的积累。 EC50 = 2.4μM(用试剂盒测量)。 |
参考文献
A phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the multi-drug resistance protein-1 (MRP-1) inhibitor sulindac, in combination with epirubicin in patients with advanced cancer
Authors: O’Connor R, O’Leary M, Ballot J, Collins CD, Kinsella P, Mager DE, Arnold RD, O’Driscoll L, Larkin A, Kennedy S, Fennelly D, Clynes M, Crown J.
Journal: Cancer Chemother Pharmacol (2007): 79
Mutational Patterns Associated with the 69 Insertion Complex in Multi-drug-resistant HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase that Confer Increased Excision Activity and High-level Resistance to Zidovudine
Authors: Cases-Gonzalez CE, Franco S, Martinez MA, Menendez-Arias L.
Journal: J Mol Biol (2007): 298
A case of multi-drug resistant recurrent breast cancer with multiple bone metastasis responding to TS-1 and trastuzumab
Authors: Nakajima H, Mizuta N, Mizuta M, Nakatsukasa K, Kobayashi A, Hachimine Y, Sakaguchi K, Fujiwara I, Sawai K.
Journal: Gan To Kagaku Ryoho (2006): 1305
A controlled clinical trial of long course chemotherapy regimens containing rifabutin in the treatment of multi-drug resistant pulmonary tuberculosis
Authors: Zhu LZ, Fu Y, Chu NH, Ye ZZ, Xiao HP, Wang W, Yuan SL, Zhang X, Luo YA, Ma LP.
Journal: Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi (2006): 520
Activity-guided isolation of scopoletin and isoscopoletin, the inhibitory active principles towards CCRF-CEM leukaemia cells and multi-drug resistant CEM/ADR5000 cells, from Artemisia argyi
Authors: Adams M, Efferth T, Bauer R.
Journal: Planta Med (2006): 862
Advances in the study of drugs for the treatment of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis
Authors: Tang SJ.
Journal: Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi (2006): 567
Assessment of resistance in multi drug resistant tuberculosis patients
Authors: Irfan S, Hassan Q, Hasan R.
Journal: J Pak Med Assoc (2006): 397
Bacteriologic profile of bacteremia due to multi-drug resistant bacteria at Charles-Nicolle Hospital of Tunis
Authors: Saidani M, Boutiba I, Ghozzi R, Kammoun A, Ben Redjeb S.
Journal: Med Mal Infect (2006): 163
Clinical Prediction Tool to Identify Patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Tract Infections at Greatest Risk for Multi-Drug Resistance
Authors: Lodise TP, Miller CD, Graves J, Furuno JP, McGregor JC, Lomaestro B, Graffunder E, McNutt LA.
Journal: Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2006)
Colistin, meropenem and rifampin in a combination therapy for multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii multifocal infection
Authors: Biancofiore G, Tascini C, Bisa M, Gemignani G, Bindi ML, Leonildi A, Giannotti G, Menichetti F.
Journal: Minerva Anestesiol. (2006)