上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
CytoTell 活细胞染色红色 590
 |
货号 | 22262 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 2×500 Tests | 价格 | 3264 | |
| Ex (nm) | 562 | Em (nm) | 587 | |
| 分子量 | 619.53 | 溶剂 | DMSO | |
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
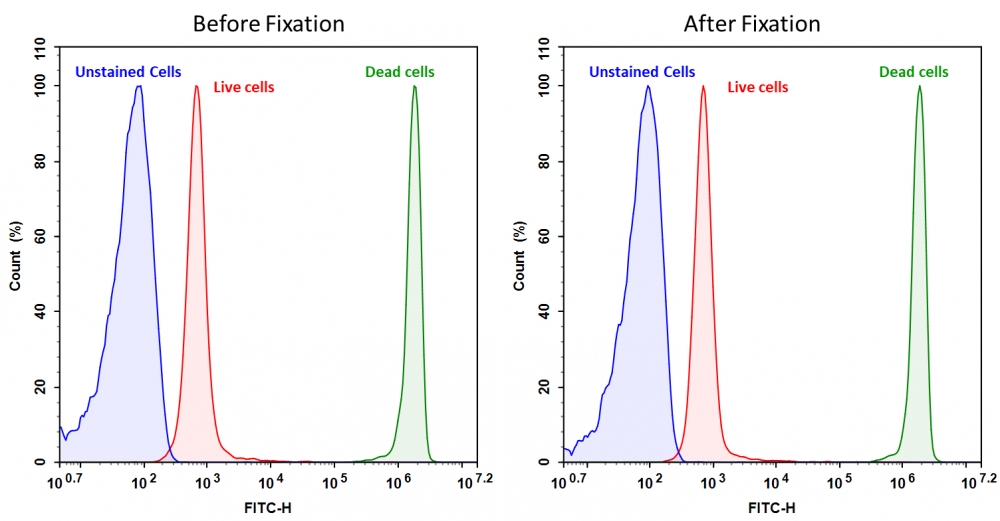
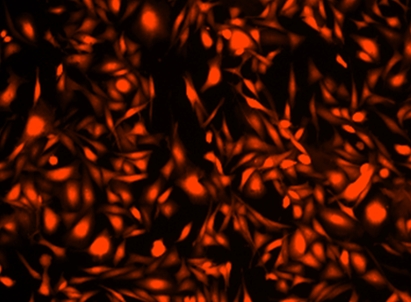
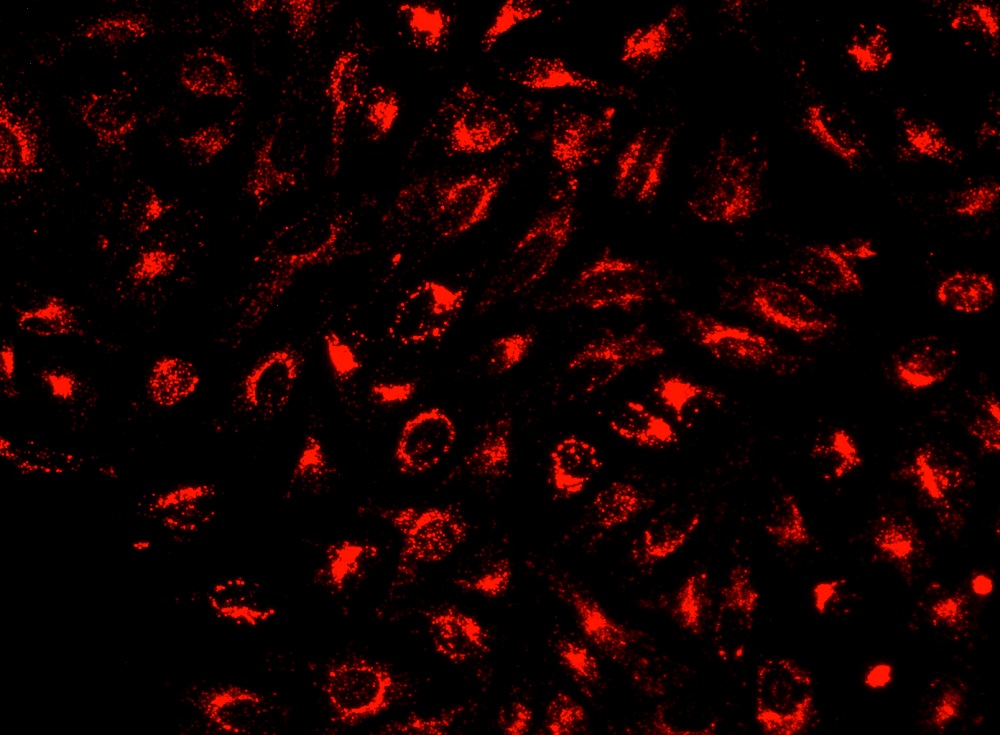
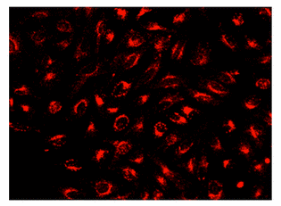
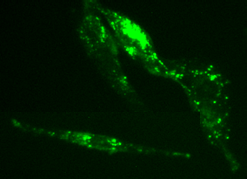
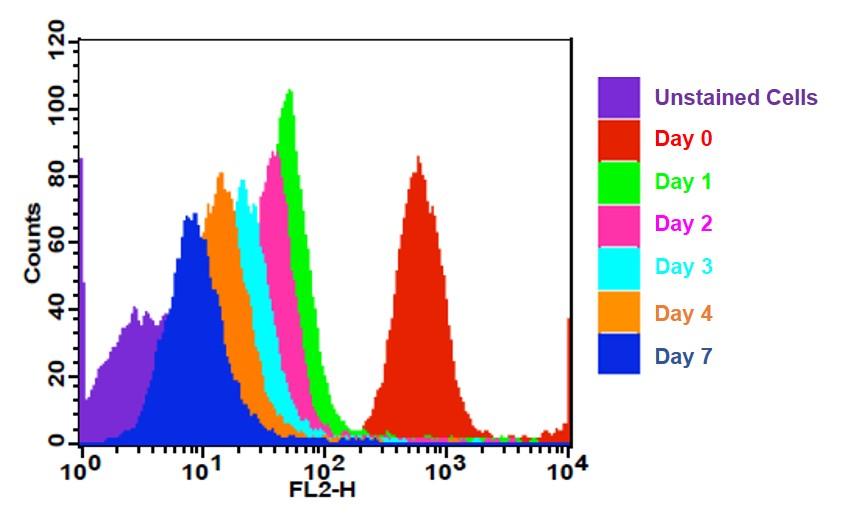
CytoTell 活细胞染色红色 590是美国AAT Bioquest生产的用于活细胞染色的探针,流式细胞仪结合荧光染色是一个强大的分析异质细胞群工具。在所有现有的荧光染料CFSE是一种广泛用于活细胞分析的优选细胞增殖的指标。然而,这是不可能用CFSE及其荧光素类似物的GFP转染的细胞,或为其中一个FITC标记的抗体用于自CFSE及其荧光素类似物,具有的激发和发射光谱几乎相同。 CytoTell 染料是主要的激光线,如405纳米, 488纳米或633纳米多色排放。 CytoTell 染料具有最小的细胞毒性,并且是用于多色应用与任何GFP的细胞系或FITC-标记的抗体,它们激发或发射光谱的荧光明显不同。 CytoTell 红色是红色荧光染料染色的细胞均匀。 CytoTell 红也可用于标记细胞的长期跟踪。分析使用两个参数的曲线可以更好的提供分辨率。细胞标记的细胞CytoTell 红可以是固定和透化的,适用于使用标准含甲醛固定剂与基于皂苷的透化缓冲液胞内靶标分析。 CytoTell 红色为630nm的激发峰,并且可以通过红色( 633纳米)的激光线激发。它具有660nm的峰值发射,可以用一个 660/20通道滤波片组(相当于APC的Alexa Fluor ® 647 ,和Cy5 ® ) ,使其与利用GFP或FITC标记的抗体的多色细胞分析中的应用兼容被检测。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的CytoTell 活细胞染色红色 590。
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| 激发: | 488 or 561nm激光 |
| 发射: | 610/20nm滤波片 |
| 推荐孔板: | PE-Texas Red通道 |
产品说明书
操作方法
1.准备500 XDMSO储备溶液
将500μLDMSO加入染料粉末小瓶中,通过涡旋混合均匀,得到500X DMSO储备溶液。
注意:应及时使用原液; 任何剩余的溶液应等分并在< -20 o C冷冻。避免反复冻融循环,避免光照。
2.准备1X染料工作溶液
制备1X 染料工作由d溶液iluting的500X DMSO储备溶液在1至500 在Hanks(HHBS)和20mM Hepes缓冲液或者您选择的缓冲液,pH 7 (如1种500X的μL DMSO储备溶液至500 μL缓冲区)使用前。通过涡旋将它们充分混合。
注意:染料工作溶液的最终浓度应根据经验确定不同的细胞类型和/或实验条件。建议在至少在折叠范围内的浓度下进行测试。例如CytoTell™Red在某些细胞类型中使用的量可能比推荐浓度少得多。
3.用流式细胞仪或荧光显微镜分析细胞:
3.1用测试化合物处理细胞一段所需的时间。
3.2离心细胞,每管取1-5×10 5个细胞。
3.3将细胞重悬于500μL 染料工作溶液中(来自步骤2)。
可选:一个可以添加500X DMSO储备溶液到细胞中的情况下直接介质除去(如,加入1种微升500X DMSO储备溶液加到500个微升细胞)
3.4在室温或37 ° C 下用染料溶液孵育细胞10到30分钟,避光。
3.5从细胞中取出染料工作溶液,用HHBS或您选择的缓冲液清洗细胞。将细胞重悬于500μL预热的HHBS或培养基中,每管获得1-5×10 5个细胞。
3.6使用流式细胞仪或荧光显微镜监测推荐的Ex / Em(见表1)的荧光变化。
参考文献
Cooperation of innate immune cells during Hepatitis C virus infection
Authors: Volker Klöss
Journal: (2017)
CXCL12–CXCR4 Axis Is Required for Contact-Mediated Human B Lymphoid and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Differentiation but Not T Lymphoid Generation
Authors: Hirohito Minami, Keiki Nagaharu, Yoshiki Nakamori, Kohshi Ohishi, Naoshi Shimojo, Yuki Kageyama, Takeshi Matsumoto, Yuka Sugimoto, Isao Tawara, Masahiro Masuya
Journal: The Journal of Immunology (2017): ji1700054
Interaction and Mutual Activation of Different Innate Immune Cells Is Necessary to Kill and Clear Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Cells
Authors: Volker Klöss, Oliver Grünvogel, Guido Wabnitz, Tatjana Eigenbrod, Stefanie Ehrhardt, Felix Lasitschka, Volker Lohmann, Alexander H Dalpke
Journal: Frontiers in Immunology (2017): 1238
Onionin A inhibits ovarian cancer progression by suppressing cancer cell proliferation and the protumour function of macrophages
Authors: Junko Tsuboki, Yukio Fujiwara, Hasita Horlad, Daisuke Shiraishi, Toshihiro Nohara, Shingo Tayama, Takeshi Motohara, Yoichi Saito, Tsuyoshi Ikeda, Kiyomi Takaishi
Journal: Scientific Reports (2016)
Multiplexing analysis of cell proliferation and cellular functions using a new multicolor panel of fluorescent cell proliferation dyes (P1290)
Authors: Jinfang Liao, Qin Zhao, Yibo Wu, Zhenjun Diwu
Journal: The Journal of Immunology (2013): 119–4
相关产品
| 产品名称 | 货号 |
| 活细胞染色 CytoTell 蓝色 | Cat#22251 |
| 活细胞染色 CytoTell 绿色 | Cat#22253 |
| 活细胞染色 CytoTell 绿色 | Cat#22240 |