上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Cell Meter TUNEL凋亡检测试剂盒 绿色荧光
 |
货号 | 22849 | 存储条件 | 在零下15度以下保存, 避免光照 |
| 规格 | 50 Tests | 价格 | 3924 | |
| Ex (nm) | 498 | Em (nm) | 522 | |
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | |||
| 产品详细介绍 | ||||
简要概述
DNA片段化代表晚期细胞凋亡的特征。凋亡细胞中的DNA断裂可以通过末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶(TdT)介导的dUTP缺口末端标记(TUNEL)检测。 TUNEL测定法依赖于DNA中存在的缺口,该缺口可通过TdT进行鉴定,TdT是一种酶,该酶催化添加标记物的dUTP。现有的所有TUNEL分析均包含剧毒的甲胂酸钠,这可能会诱导细胞凋亡并降低DNA的产生和DNA链。我们的Cell Meter TUNEL细胞凋亡测定试剂盒使用了不含甲胂酸钠的专有缓冲系统。该试剂盒基于将我们专有的荧光染料掺入凋亡过程中形成的DNA片段中。该测定法经过优化,可直接检测分离的或贴壁细胞中的细胞凋亡,而无需使用任何抗体。该试剂盒为所有必需成分提供了优化的测定方案。适用于荧光酶标仪,荧光显微镜或流式细胞仪。在流行的FITC通道上可以轻松检测到其信号。金畔生物是AAT Bioquest的中国代理商,为您提供最优质的Cell Meter TUNEL凋亡检测试剂盒。
点击查看光谱
适用仪器
| 流式细胞仪 | |
| 激发: | 488nm激光 |
| 发射: | 530/30nm滤波片 |
| 通道: | FITC滤波片 |
| 荧光显微镜 | |
| 激发: | FITC滤波片 |
| 发射: | FITC滤波片 |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色透明 |
| 荧光酶标仪 | |
| 激发: | 490nm |
| 发射: | 525nm |
| cutoff: | 515nm |
| 推荐孔板: | 黑色孔板 |
产品说明书
样品实验方案
简要概述
- 用测试化合物准备细胞。
- 与TUNEL工作溶液在37°C下孵育30分钟至1小时。
- 洗涤细胞。
- 用4%甲醛(可选)固定细胞。
- 用带FITC滤光片的荧光显微镜或带FITC通道的流式细胞仪。读取Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(截止= 515 nm)处的荧光强度。
溶液配制
工作溶液配制
将0.5μL的100X Tunnelyte Green(组分A)添加到50μL的反应缓冲液(组分B)中,使总体积为50.5μL的TUNEL工作溶液。 避光。 注意:应单独评估每个细胞系,以确定最佳细胞密度。
实验步骤
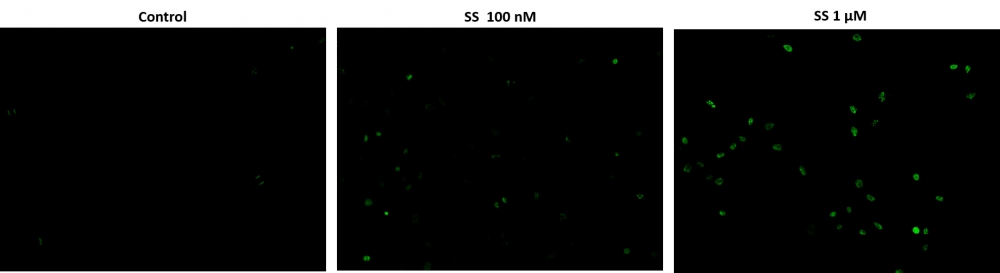
1.根据您的特定协议,将细胞培养至最佳密度以诱导凋亡。 对于在96孔板培养物中生长的贴壁细胞,我们建议大约30,000至50,000个细胞/孔,对于非贴壁细胞,建议大约1至2 x 106细胞/ mL。 同时,在每种标记条件下,用诱导群体相同的密度培养非诱导阴性对照细胞群体。 注意:我们用100 nM-1 µM星形孢菌素处理HeLa细胞4小时,以诱导细胞凋亡。
2.染色和固色:
2.1取出细胞培养基。
2.2向每个样品中添加50µL TUNEL工作溶液。
2.3在37°C下孵育30-60分钟。
2.4除去TUNEL工作溶液,并用200 µL /孔的PBS洗涤细胞1-2次。
2.5向每个样品中添加100uL反应缓冲液(组分B)。
2.6使用Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(cut off= 515 nm)的荧光酶标仪,带有FITC滤光片组的荧光显微镜或带有FITC通道的流式细胞仪检测荧光强度。
2.7可选:从步骤5中移出反应缓冲液,并向每个孔中添加100 µL /孔/ 96孔板的4%甲醛固定缓冲液(未提供)。注意:对于非贴壁细胞,请添加所需量(例如2X106细胞/ mL)的4%甲醛固定液。
2.8在室温下将平板孵育20至30分钟。
2.9去除固定剂。
2.10用PBS洗涤细胞2-3次,并用100µL PBS /孔/ 96孔板替换。
2.11使用Ex / Em = 490/525 nm(cut off= 515 nm)的荧光酶标仪,带有FITC滤光片组的荧光显微镜或带有FITC通道的流式细胞仪检测荧光强度。
2.12可选:用1X Hoechst(组分C)在Ex / Em = 350/460 nm处染色细胞核,以进行图像分析
参考文献
Vaccarin alleviates hypertension and nephropathy in renovascular hypertensive rats
Authors: Cai, Weiwei and Zhang, Zhenpeng and Huang, Yiqi and Sun, Haijian and Qiu, Liying
Journal: Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine (2018): 924–932
CO-releasing molecules-2 attenuates ox-LDL-induced injury in HUVECs by ameliorating mitochondrial function and inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Authors: Sun, Hai-Jian and Xu, Dong-Yan and Sun, Yi-Xin and Xue, Tong and Zhang, Chen-Xing and Zhang, Zhi-Xuan and Lin, Wei and Li, Ke-Xue
Journal: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2017)
Salusin-β mediates high glucose-induced endothelial injury via disruption of AMPK signaling pathway
Authors: Zhu, Xuexue and Zhou, Yuetao and Cai, Weiwei and Sun, Haijian and Qiu, Liying
Journal: Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications (2017)
Vaccarin protects human microvascular endothelial cells from apoptosis via attenuation of HDAC1 and oxidative stress
Authors: Zhu, Xuexue and Lei, Yueyue and Tan, Fanggen and Gong, Leilei and Gong, Haifeng and Yang, Wei and Chen, Ting and Zhang, Zhixuan and Cai, Weiwei and Hou, Bao and others
Journal: European Journal of Pharmacology (2017)
Axl is required for TGF-β2-induced dormancy of prostate cancer cells in the bone marrow
Authors: Yumoto, Kenji and Eber, Matthew R and Wang, Jingcheng and Cackowski, Frank C and Decker, Ann M and Lee, Eunsohl and Nobre, Ana Rita and Aguirre-Ghiso, Julio A and Jung, Younghun and Taichman, Russell S
Journal: Scientific Reports (2016)
Growth Arrest-Specific 6 (GAS6) Promotes Prostate Cancer Survival by G1 Arrest/S Phase Delay and Inhibition of Apoptotic Pathway During Chemotherapy in Bone Marrow
Authors: Lee, Eunsohl and Decker, Ann M and Cackowski, Frank C and Kana, Lulia A and Yumoto, Kenji and Jung, Younghun and Wang, Jingcheng and Buttitta, Laura and Morgan, Todd M and Taichman, Russell S
Journal: Journal of cellular biochemistry (2016)
RFX1–dependent activation of SHP-1 induces autophagy by a novel obatoclax derivative in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Authors: Su, Jung-Chen and Tseng, Ping-Hui and Hsu, Cheng-Yi and Tai, Wei-Tien and Huang, Jui-Wen and Ko, Ching-Huai and Lin, Mai-Wei and Liu, Chun-Yu and Chen, Kuen-Feng and Shiau, Chung-Wai
Journal: Oncotarget (2014): 4909
In situ detection of apoptosis by the TUNEL assay: an overview of techniques
Authors: Loo DT.
Journal: Methods Mol Biol (2011): 3
Testicular apoptosis after dietary zinc deficiency: ultrastructural and TUNEL studies
Authors: Kumari D, Nair N, Bedwal RS.
Journal: Syst Biol Reprod Med (2011): 233
In situ localization of apoptosis using TUNEL
Authors: Hewitson TD, Darby IA.
Journal: Methods Mol Biol (2010): 161
